Who gets head lice? 
- Almost anyone can get head lice.
- Head lice are not a health hazard or a sign of poor hygiene.
- Children attending preschool or elementary school, and those who live with them, are the most commonly affected.
How do head lice spread?
- Most are spread by head to head contact.
- Head lice cannot jump or fly.
- They cannot live for long off of a human head.
- Dogs, cats and other pets do not spread lice.
What do Head Lice look like?
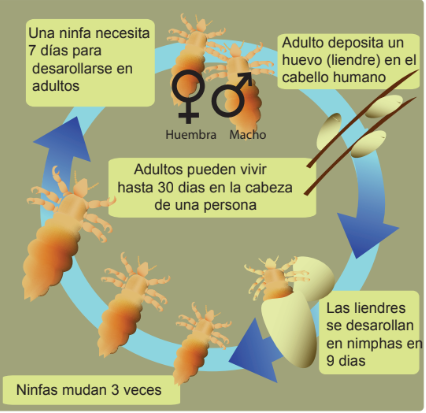
- Nits (eggs) - are teardrop shaped, attached to the hair shaft, yellowish or white, are often confused with dandruff but they cannot be brushed off as they stick to the hair shaft.
- Nymph (baby louse) - grow to adult size in 1-2 weeks, are found on the scalp or in the hair.
- Adult louse - are the size of a sesame seed, are tan to grayish-white, are commonly found behind the ears and near the neckline.

 How is Head Lice treated?
How is Head Lice treated?
- If head lice are suspected, families should consult a healthcare provider as soon as possible.
- Treatment considerations include:
- Over the counter treatments are available, but some resistance to these products has been reported.
- There is no scientific evidence that home remedies are effective.
- There are prescription treatment options available - contact your healthcare provider to determine what is appropriate for your family.
- Do not use the selected lice treatment more often than recommended on the package or by your healthcare provider.


All household members and other close contacts should be checked
- Anyone with evidence of an active lice infestation should be treated.
- All persons with active head lice should be treated at the same time.
 What about cleaning?
What about cleaning?
- Adult head lice survive less than 1-2 days, and nits (head lice eggs) generally die within a week once they fall off a person and cannot feed.
- Vacuum floor and furniture where infested person sat or lay.
- Fumigants or fogs are NOT necessary and may be dangerous if inhaled or absorbed through the skin.
- Family bed linens and recently used clothes, hats and towels, as well as personal articles such as toys, combs, brushes and hair clips should washed in very hot water or sealed in a plastic bag for 2 weeks.
What if the treatment didn't work? Here are some reasons the treatment might not have worked:
- The directions on the treatment product were not followed closely enough.
- The nits were not completely removed.
- The child got head lice again from a playmate.
- Lice may not die right away.
- The problem was not lice.
- Some lice are resistant to the over the counter treatment and you should talk to your pediatrician about a prescription treatment.




 How is Head Lice treated?
How is Head Lice treated?

 What about cleaning?
What about cleaning?
